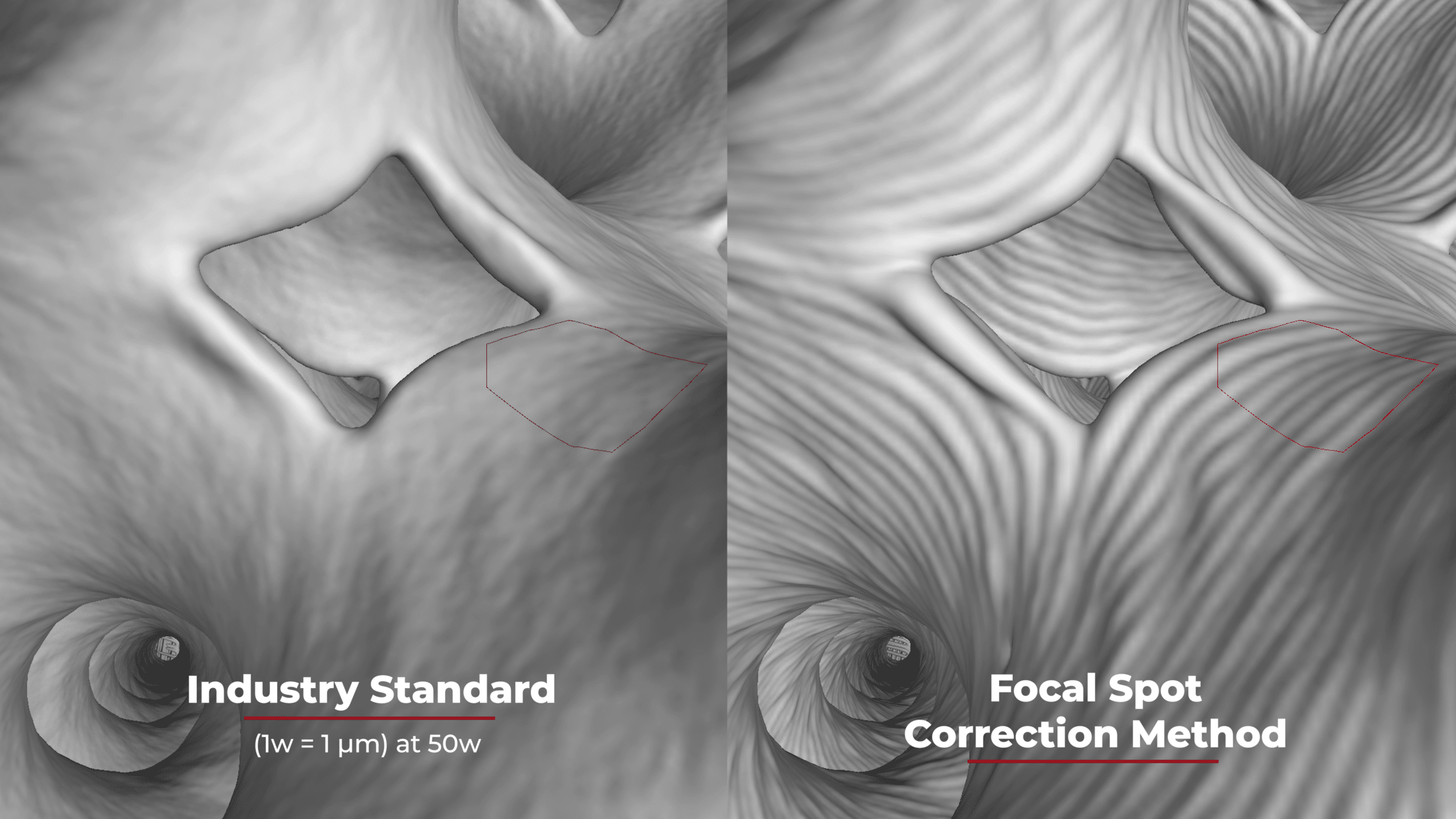
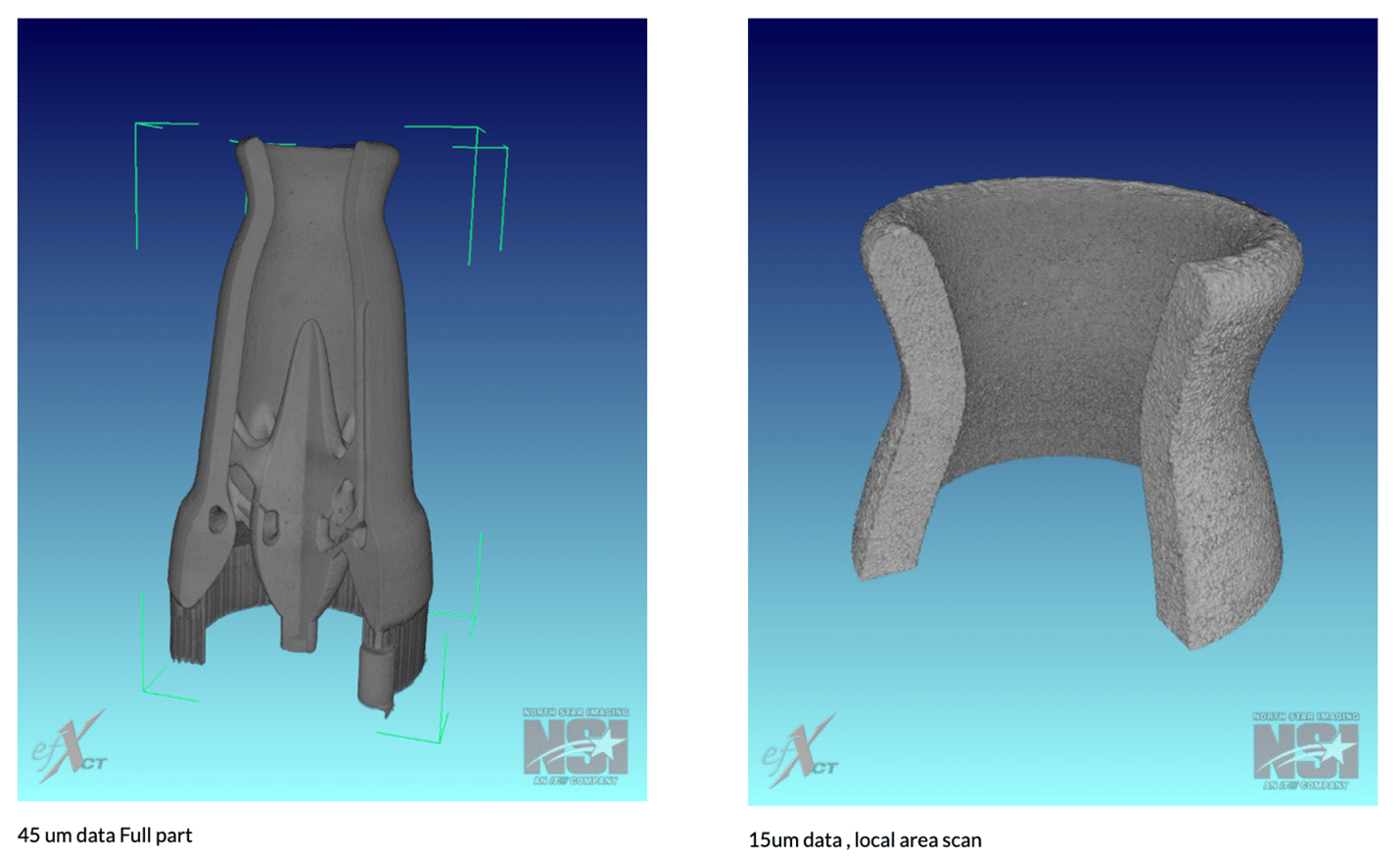
Using X-ray Systems for Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering deconstructs an object through a non-destructive technique to analyze its internal structure, design and functionality. It is a vital process used across various industries as it helps engineers and manufacturers improve their production methods and existing designs of products. Scientists can conduct reverse engineering through several different techniques, but X-ray systems are a favorable tool because of their non-invasive, powerful inspection methods. This blog post will provide an overview of reverse engineering and the benefits of using X-ray systems.
What is Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering aims to analyze how a device, process or system functions. It studies an object’s internal components and structures and the interaction between them. Reverse engineering is crucial as it enables engineers and manufacturers to conduct failure analysis, fault isolation and vulnerability of a pre-existing product and understand how a system works and how to improve it. In previous years, reverse engineering could be a costly and time-consuming process. Still, with the technological advances and use of X-ray systems (and X-ray Microscopy (XRM)), it has become more efficient and valuable.
How are X-ray Systems Used for Reverse Engineering?
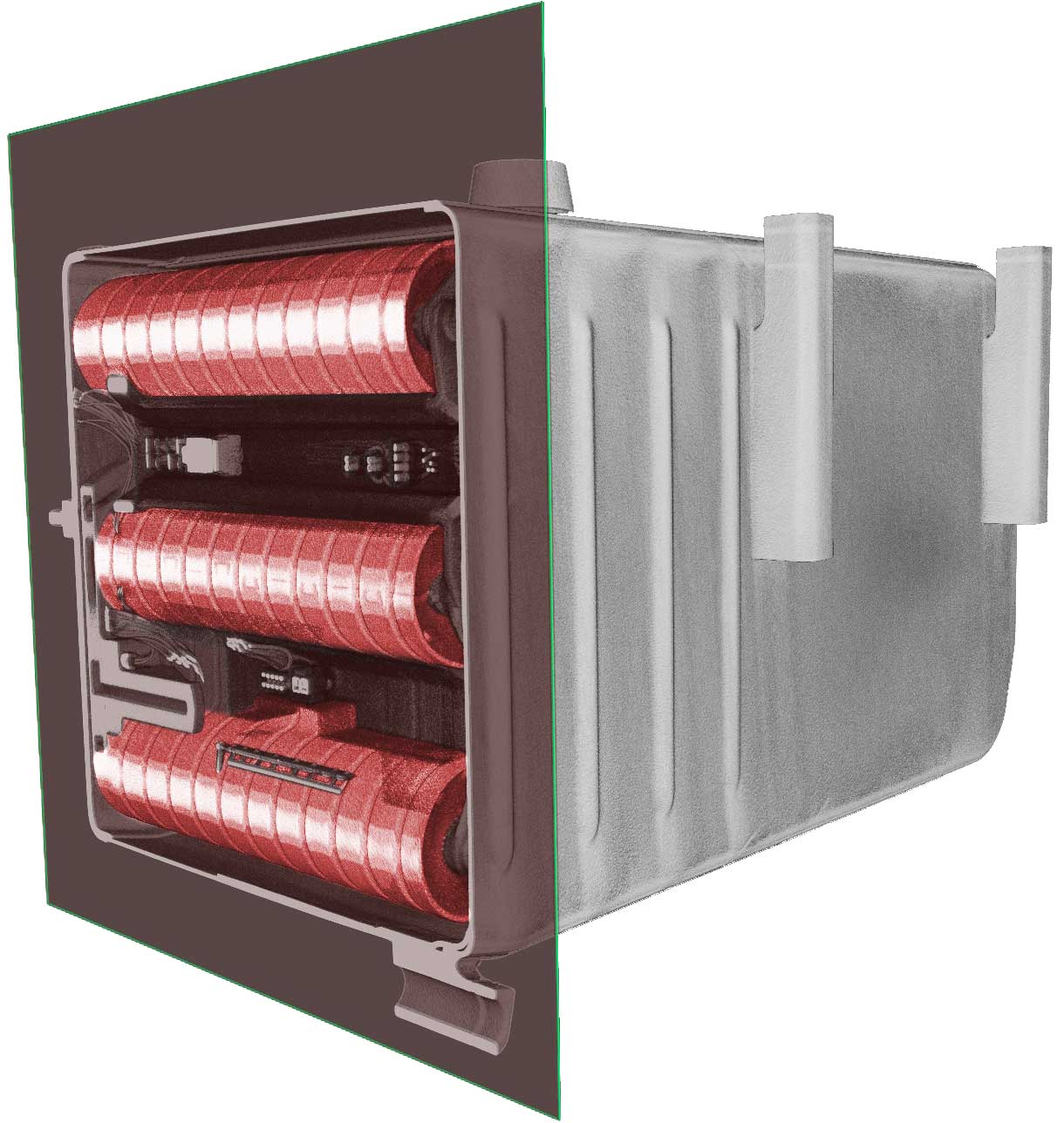
Several methods are available for reverse engineering, but X-ray systems are becoming a preferred option for many reasons. We will discuss its benefits in more detail in the following sections. X-ray systems use high-energy electromagnetic radiation beams to penetrate a sample, enabling the researcher to capture images non-invasively and analyze, measure and inspect a sample’s internal aspects. This is conducted by placing a sample on a rotating platform and taking scans of it from different angles, and then using software to reconstruct the scans into 2D and 3D reconstructed images.
The primary reasons for using X-ray inspection systems include
- Analyzing and measuring internal components and structures
- Identifying contaminants
- Identifying cracks, fractures and other damages
- Measuring components, their inclusions, porosity and thickness
Benefits of X-ray Systems
X-ray systems are powerful tools that are invaluable to many applications and industries. In reverse engineering, X-ray systems have enhanced a once laborious process into a more streamlined and beneficial one. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical significantly benefit from reverse engineering, especially with X-ray systems, as manufacturers can study the configuration and functionality of existing products to test the quality and safety and improve them if necessary.
There are many benefits to choosing X-ray systems for reverse engineering, and they include the following:
- Functionality: Understanding how a sample works
- Generating CAD files from 3D images, which is required in many manufacturing methods
- Improved image quality and accuracy
- Improvements: Making changes or improvements to existing systems
- Meet customer requirements
- Quality: Analyzing and testing the quality of a sample
- Safety: Ensuring the sample meets compliance standards
- Staying ahead of the competition
Reverse engineering is an integral part of industrial manufacturing, and improving its efficiency and accuracy with X-ray systems is crucial to developing safer and more suitable products.
North Star Imaging: X-ray Systems
North Star Imaging offers clients a wide range of X-ray systems for various industrial applications. We provide 2D digital X-ray radiography systems, 3D X-ray computed tomography systems and high-energy X-ray systems, all of which come with exceptional accuracy and resolution, integrated software and automation options.
Contact a member of North Star Imaging today to learn more about how X-ray systems can enhance your reverse engineering processes.
Resources
- https://dforte.ece.ufl.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/65/2020/08/ISTFA_2015_PCB-RE-final.pdf