Did you try binning it?
What is pixel binning?
Pixel binning is a mode that the X-ray detector can run in that takes a 2×2 matrix of pixels and combines them to create one larger pixel. This is done in the hardware internally in the detector so there is no additional processing time for the computer. There are a number of benefits to using pixel binning including better signal level, higher contrast, and faster framerates. The down side to using pixel binning is that there is a loss in image resolution. This decrease in resolution may not have much of a negative effect though, as the contrast sensitivity that is gained may be more beneficial.
Contrast sensitivity/signal improvements
Contrast sensitivity is increased when running the detector in pixel binning mode. The increase in signal level from the larger effective pixel helps create more contrast sensitivity. This is particularly useful when scanning a hard to penetrate sample because it gives you that little boost in contrast to allow you to see smaller defects that you might not have had enough contrast to detect without pixel binning. Higher signal level also allows you to back the detector off away from the tube to reduce cone beam artifacts. This can be very useful when scanning in order to create a clean surface or for measurements.
Speed
Because the pixel binning is done within the hardware of the detector, there is less data to transfer to the computer. This allows the detector to run at much higher frame rates than is possible without pixel binning, approaching or exceeding “real time” or around 30fps. Also, the increase in signal means that you can actually use those higher frame rates for your scan, allowing you to use more frame averaging to further reduce noise in the image.
Resolution loss
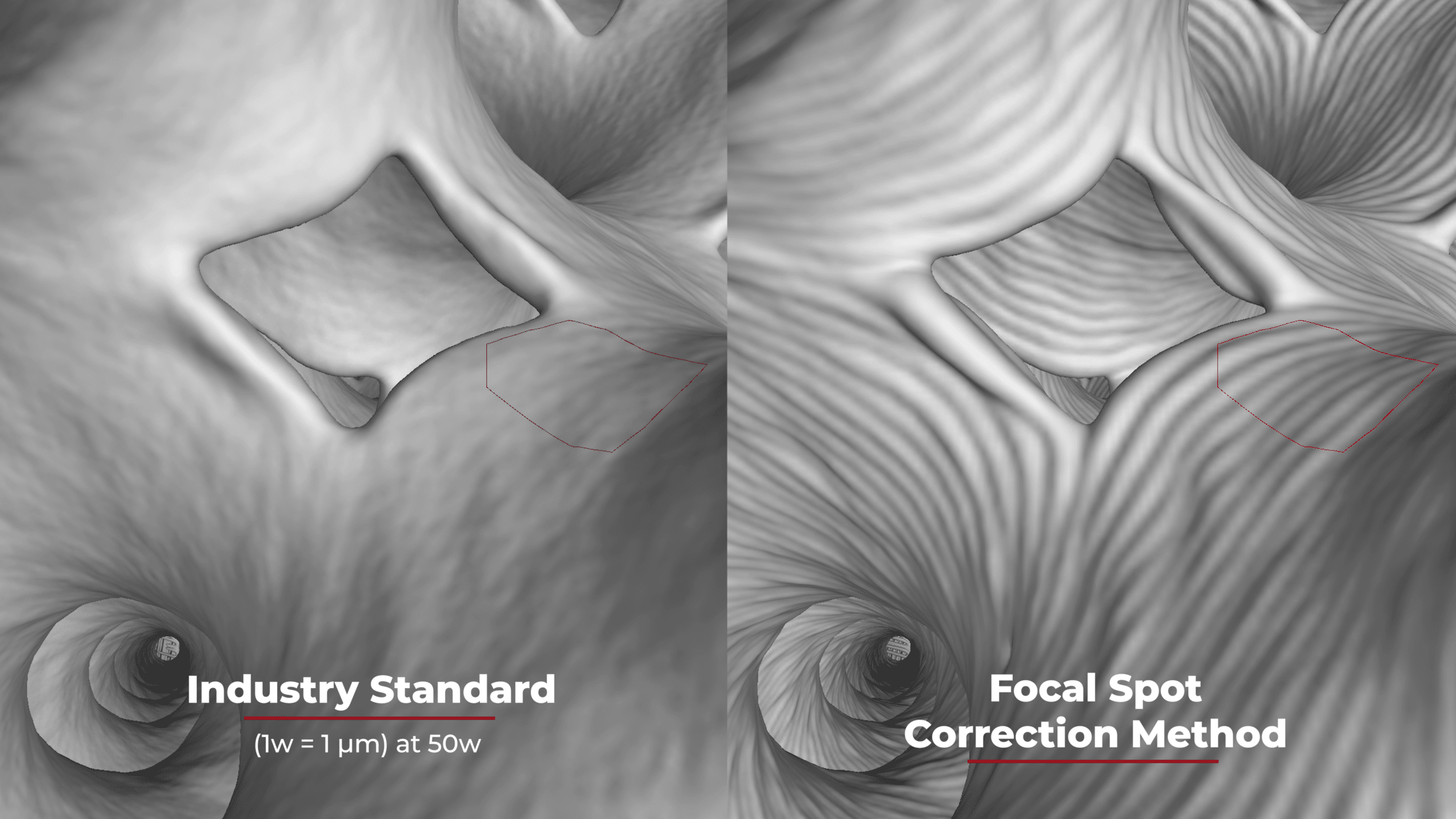
Putting your detector into pixel binning mode causes some loss in image resolution. This is caused by the detector taking a 2×2 pixel matrix and adding the values together. This does not, however, mean that your detectable defect size doubles. A typical 127µm pixel pitch detector may have a SRb value of 170-180µm, but if you take that same detector and put it in pixel binning mode you do not get a SRb of 340-360µm, you actually get a SRb of around 250µm. That is only roughly a 40% decrease in spatial resolution. This means that using pixel binning is not as bad for resolution as most people think.
Combining with new technology like SubpiX
On some applications the decrease in image resolution when using pixel binning means that there simply will not be enough pixels representing the indication, and without pixel binning there isn’t enough contrast sensitivity to detect the indication. In those applications it can be advantageous to combine pixel binning with SubpiX to get the benefits of pixel binning and not have a loss in resolution. With the higher frame rates and higher signal levels from pixel binning the SubpiX scans can be substantially faster than scans with full resolution.